Internal Training
Technical Foundation
During this internship, I received quick training on various technologies that I could use for my future missions. These technologies offer a broad technical foundation to address different possible tasks.
This foundation is based on:
Angular: An open-source TypeScript framework compatible with JavaScript and maintained by Google, used for web development. It relies on a component-based architecture, where different parts of the user interface (UI) are encapsulated in reusable and independent components. Angular is often used in the development of single-page applications (SPA) or progressive web applications (PWA).

Source: Angular
Spring: An open-source Java framework for creating microservices and web applications. It also allows for the development of data processing applications, such as ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, batch processing, and event processing.
Source: Spring
Kafka: An open-source distributed streaming platform designed to handle real-time data streams, used for real-time processing, log collection, data pipeline construction, and data integration. Kafka operates on message transactions between producers and consumers, with a partitioned architecture for ordered message storage.

Source: Kafka
Spark: A powerful framework that allows for the rapid and efficient processing and analysis of vast datasets, seamlessly integrating with Kafka to ensure a continuous and high-performance flow of information.
Source: Spark
Elasticsearch: An open-source search and analytics engine that enables real-time searches and analyses with a distributed and scalable architecture, capable of handling enormous volumes of data.
Kibana: A data visualization and exploration tool designed to work with Elasticsearch, allowing the creation of interactive and customizable dashboards that display real-time data visualizations.


Source: Elastic
Example
We can summarize these technologies with a concrete example:
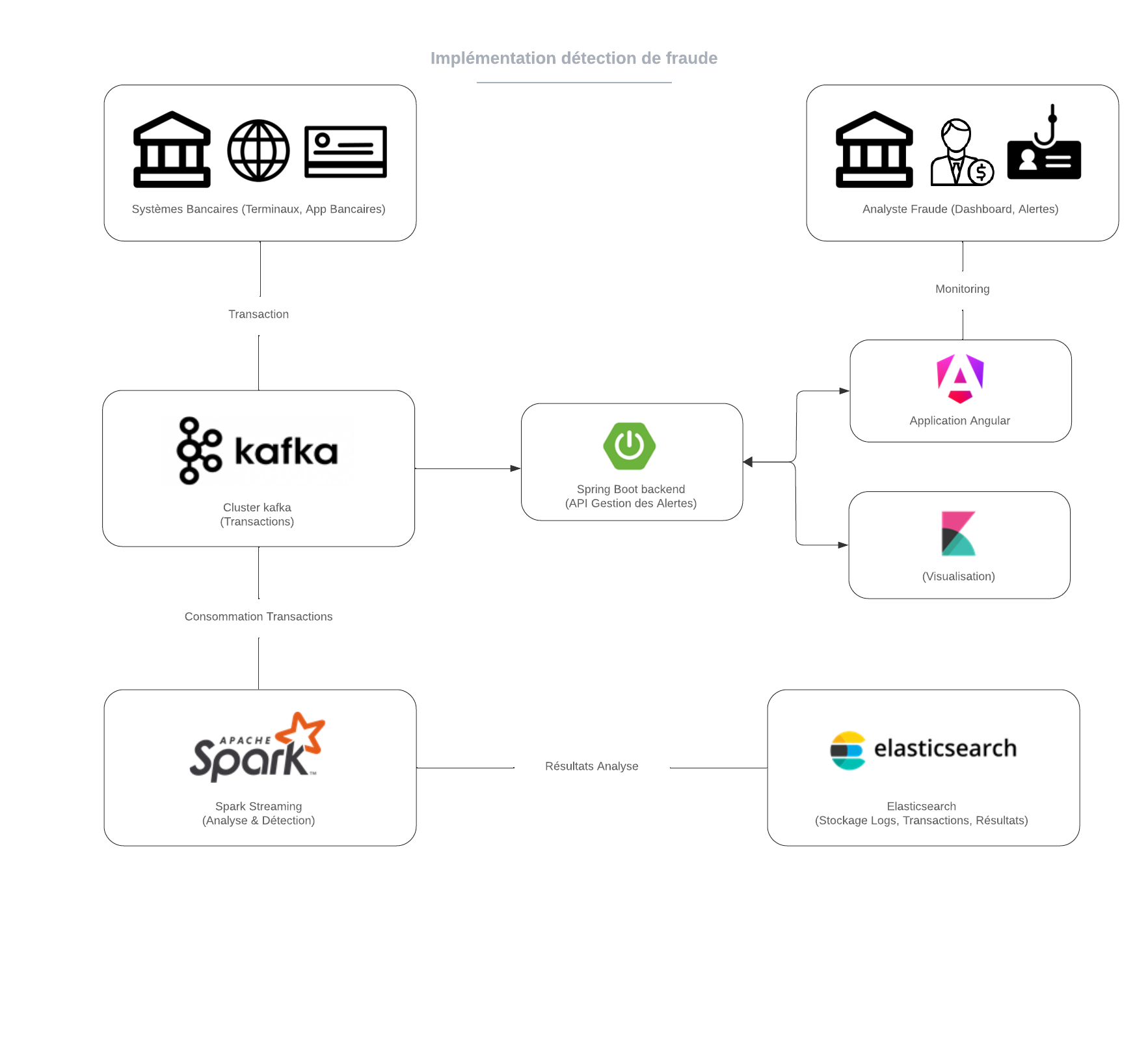
In this example, we want to implement a fraud detection and analysis system:
- For this, banking transactions are captured via terminals or banking applications and then sent to a Kafka cluster for real-time processing.
- The transactions are then consumed by Apache Spark, which performs analyses to detect fraudulent behavior.
- The results of these analyses are stored in Elasticsearch, allowing for quick search and visualization via Kibana.
- A Spring Boot backend manages the generated alerts, while an Angular application allows analysts to monitor transactions and visualize results through interactive dashboards.
- This integrated system ensures effective fraud detection and real-time data analysis.

